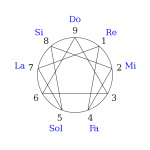
The Enneagram defines nine interconnected personality typologies, sometimes called “enneatypes”, which are represented by the points of a geometric figure called an enneagram.
G. I. Gurdjieff is credited with making the word enneagram and the enneagram figure commonly known – see Fourth Way enneagram. He did not, however, develop the nine personality types associated with the Enneagram of Personality.
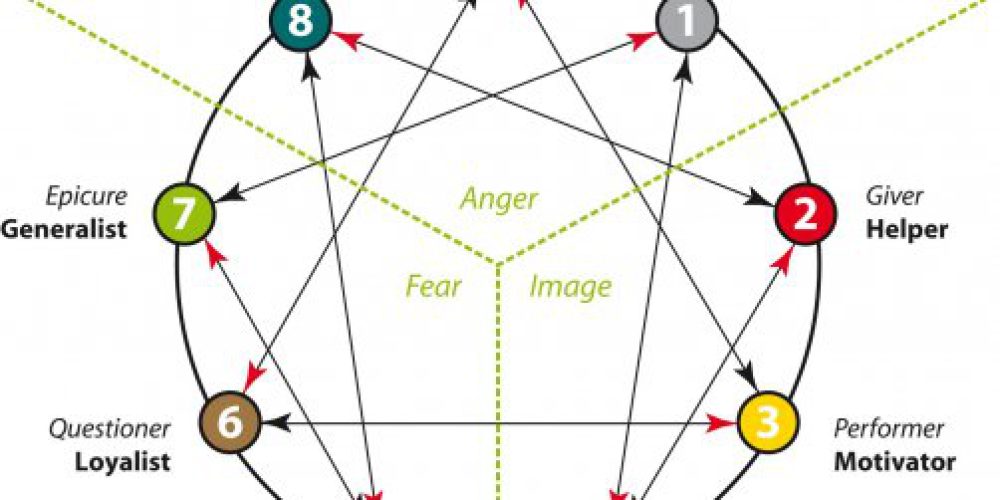
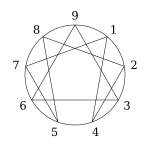
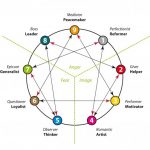
The enneagram figure is usually composed of three parts; a circle, an inner triangle (connecting 3-6-9) and an irregular hexagonal “periodic figure” (connecting 1-4-2-8-5-7). According to esoteric spiritual traditions, the circle symbolizes unity, the inner triangle symbolizes the “law of three” and the hexagon represents the “law of seven” (because 1-4-2-8-5-7-1 is the repeating decimal created by dividing one by seven in base 10 arithmetic), These three elements constitute the usual enneagram figure.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enneagram_of_Personality
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourth_Way_enneagram
- https://app.box.com/s/sxpwvqt269epckcddr50cbtaafevbhfu [9 typologies PDF]
Enneagram of Personality theorists teach that a person’s basic type is modified, at least to some extent, by the personality dynamics of the two adjacent types as indicated on the enneagram figure. These two types are often called “wings”. A person with the Three personality type, for example, is understood to have points Two and Four as their wing types. The circle of the enneagram figure may indicate that the types or points exist on a spectrum rather than as distinct types or points unrelated to those adjacent to them. A person may be understood, therefore, to have a core type and one or two wing types that influence but do not change the core type.
For Enneagram theorists the lines connecting the points add further meaning to the information provided by the descriptions of the types. Sometimes called the “security” and “stress” points, or points of “integration” and “disintegration”, some theorists believe these connected points also contribute to a person’s overall personality. From this viewpoint, therefore, at least four other points affect a person’s overall personality; the two points connected by the lines to the core type and the two wing points.
Each of the personality types is usually understood as having three “instinctual subtypes”. These subtypes are believed to be formed according to which one of three instinctual energies of a person is dominantly developed and expressed. The instinctual energies are usually called “self-preservation”, “sexual” (also called “intimacy” or “one-to-one”) and “social”. On the instinctual level, people may internally stress and externally express the need to protect themselves (self-preservation), to connect with important others or partners (sexual), or to get along or succeed in groups (social). From this perspective, there are twenty-seven distinct personality patterns, because people of each of the nine types also express themselves as one of the three subtypes.